What is an Audit
An audit is the examination of the financial report of an organisation - as presented in the annual report - by someone independent of that organisation. The financial report includes a balance sheet, an income statement, a statement of changes in equity, a cash flow statement, and notes comprising a summary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory notes.
Our Approache
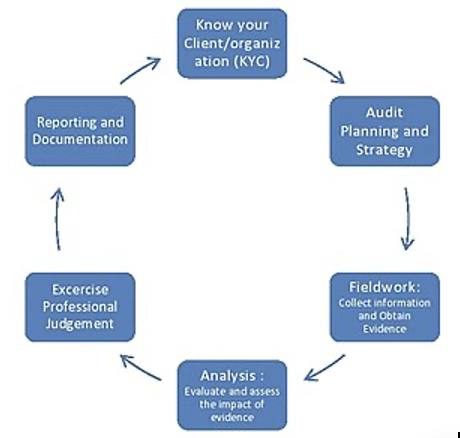
The key aspects of auditing in accounting are:
Objective Verification
Auditors independently verify financial statements and records to ensure they reflect the true financial position of the company.
This involves checking the accuracy of financial transactions, balances, and disclosures.
Compliance with Standards
Auditing ensures that financial statements are prepared in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), as applicable.
Compliance with these standards helps maintain consistency and reliability in financial reporting.
Internal Controls Assessment
Auditors evaluate the effectiveness of an organization's internal controls over financial reporting.
This includes assessing processes and procedures designed to prevent and detect errors and fraud.
Risk Management
Auditing helps identify and assess financial risks that could impact the organization.
Auditors provide recommendations to mitigate these risks and enhance the overall risk management framework.
Fraud Detection
Auditors look for signs of fraud or financial irregularities.
They conduct tests and procedures to detect any misrepresentations or intentional errors in the financial statements.
Stakeholder Confidence
An independent audit enhances the credibility of financial statements, providing assurance to investors, creditors, regulators, and other stakeholders.
This trust is crucial for securing financing, complying with regulatory requirements, and maintaining a good reputation.
Continuous Improvement
Auditors provide feedback on areas where the organization can improve its financial processes and controls.
This helps organizations enhance their financial practices and operational efficiency over time.
Type of audit engagements we perform:
- External (Statutory) Audits
- Internal Audits
- Assurance and special audits
An engagement in which a practitioner expresses a conclusion designed to enhance the degree of confidence of the intended users other than the responsible party about the outcome of the evaluation or measurement of a subject matter against criteria.
Assurance engagement refers to a systematic process conducted by independent professionals to provide credibility and reliability to financial information. The primary aim is to enhance investor confidence by ensuring that financial statements and related information are accurate, transparent, and in compliance with relevant regulations.
Assurance engagements are crucial for various reasons. They help investors make informed decisions by offering assurance of the accuracy of financial statements, reducing the risk of misleading information. This is particularly vital in investment decision-making, as accurate financial reporting contributes to a clearer understanding of a company's financial health.
To ensure that our audits are in accordance with the requirements of International Standards on Auditing our firm uses the following audit systems: